Zinc Die Casting vs. Other Processes in Medical Device Production
Zinc Die Casting vs. Other Processes in Medical Device Production
Blog Article
Selecting the most appropriate production method is critical to the success of a medical device because of its high precision and cost efficiency requirements. In a surgical procedure, for instance, pieces that need to be either implanted or used must have great reliability and be fabricated with utmost precision, which is only achievable with appropriate medical device manufacturing techniques.
While there are many production approaches, zinc die casting distinguishes itself from the rest with its incorporation into a broader competition installing robust machining and injection molding alongside 3D printing. The purpose of this article is to research the differences between zinc die casting and other technologies in the context of medical device manufacturing.
We will look at each process in creating intricate geometries, mechanical properties, cost-efficiency, and how well it caters to the parameters of the medical field. For medical device manufacturers, high-strength parts, exact accuracy, and swift prototyping all pose varying demands. Let us begin exploring which processes can suit multiple medical device needs.
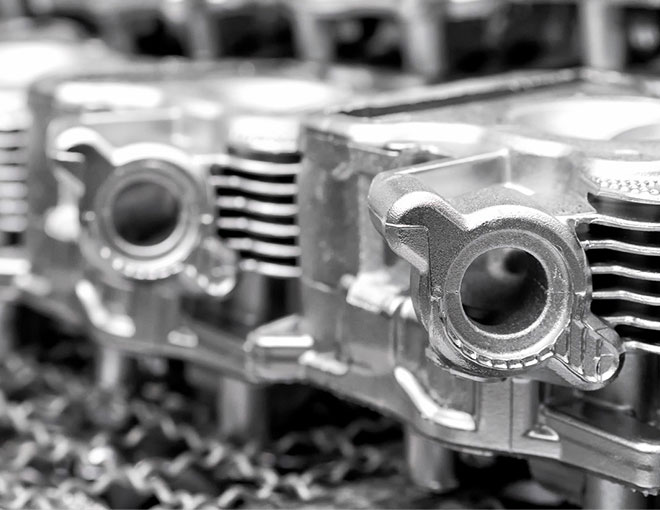
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting:
Complex geometries: Components with internal cavities, undercuts, and thin walled structures can be easily casted, which reduces the need for many assembled parts. Interpolated surfaces are done quickly and through fewer steps so time is minimized.
Cost-effective for high volumes: In large-scale production, zinc die casting becomes more cost-effective than machining. Although the tooling costs are high for die casting, they are spread over a larger number of parts, resulting in lower per unit costs.
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting:
Zinc die casting’s restrictions to zinc-based alloys as its primary material suggests a constrained ability to utilize numerous metals, plastics, and composites that are more readily available through machining. Unlike them, zinc-based alloys offer reasonable characteristics for several medical uses. While die casting or injection molding has its benefits, machining is able to achieve very high-quality surface finishes. However, in certain medical applications where a smooth and precise surface is imperative, additional finishing operations are often necessary for die-cast parts.
Benefits of Zinc Die Casting:
In comparison to parts made from injection molded plastics, zinc die cast parts have greater strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. As such, these components are more effective for devices that need to withstand mechanical load, elevated temperatures, or harsh environmental conditions. Zinc die cast parts also have greater shrinkage stability during solidification which results in better accuracy and fit for medical device components, demonstrating better dimensional stability than many plastics.
Drawbacks of Zinc Die Casting:
Weight: Medical devices that have portable features may prefer injection molded plastics over zinc die cast parts as they are lighter. This is because zinc die casting is denser than most plastics.
Design Options: Medical devices can be user friendly and aesthetically pleasing with proper branding and usability features. In these aspects, injection molding is more capable in terms of color, transparency and incorporating soft-touch or elastomeric features which contributes to a user friendly design.
Benefits of Die Casting Zinc Components:
Volume and Speed of Production: In terms of high volume production, 3D printing is much slower than zinc die casting. Therefore, zinc die casting is more preferable in manufacturing medical devices as it is faster in producing parts.
Mechanical characteristics: For components that need to sustain a lot of load in medical devices, die cast zinc parts are optimal as they are load bearing components. These components are much more efficient than other components and rely on 3D printed materials.
Drawbacks of Zinc Die Casting:
Freedom of design: 3D printing offers advanced customization and complex geometrical features due to higher design freedom. It can produce advanced lattice patterns, complex internal passage ways, and other distinct geometrical forms which are difficult or impossible to produce using die casting.
Prototyping: In most cases, 3D Printing provides a faster solution to prototyping compared to casting since they can quickly generate single or short run pieces with very little tooling. The same does not apply with zinc die casting where there is a considerable amount of investment and lead time required for tooling manufacturing.
Report this page